
Stem Cell
Since leukemia was officially diagnosed in 1845, leukemia
had been an incurable disease for a long time. More than 232,000 people in the U.S. are living with leukemia and 50,000 people are being diagnosed last year. Estimated by National Cancer Institute, there were around 28,000 deaths due to leukemia in the year 2013. [54] [55]
Patients who suffered from leukemia have rapidly increasing amount of immature white blood cells in their bodies. Those abnormal white blood cells do not have the ability of keeping a functional blood system and will eventually cause problem in human organs.
Due to the large amount of abnormal white blood cells that crowed out the healthy blood cells, leukemic patients do not tend to have enough developed white cells to block viral invasion or to keep blood system functioning. Consequently, leukemic patients have to suffer from infective fever or anemia due to scarce of healthy blood cells such as red blood cells and platelets. [56]
Leukemia can now be treated by using chemotherapy, medical radiation therapy, hormone treatment and bone marrow transplant but bone marrow transplant is the only recognized way to leukemia once and for all. The key of treating leukemia is to get rid of the abnormal blood cells and restrain them from taking over the healthy system, both chemotherapy and medical radiation therapy can do the job.
The discovery of stem cells made the bone marrow transplant became true in 1968. In the case of bone marrow transplant, doctors first use chemotherapy and medical radiation to kill the abnormal blood cells and then plant healthy blood forming stem cell, from a match donator example in leukemic patients’ bloodstream. The best kind of stem cell used in bone marrow transplant is the Umbilical cord blood stem cell. Those less developed stem cell discarded by infants have less possibility to be rejected by patients, which makes them a good solution of bone marrow transplant.[57] [58]
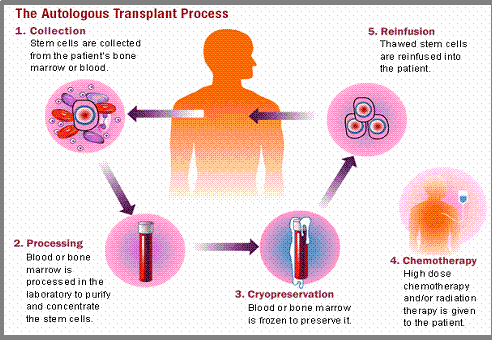
Survival rate after the bone marrow transplant is depending on the type of transplant. But if the stem cell example came from patient’s own body, the survival rate after the surgery will be nearly 90%. [57]
Citation: 54, 55, 56, 57, 58
Drug testing:
When majority of researches focus on stem cell’s ability of differentiate, the usage of stem cell already rooted in area of drug testing. Started in 2010, biological companies began to test drugs by using stem cells. Human pluripotent cell lines are the new star in drug testing area, the differentiate ability of stem cell allows scientists to control the type of cell they would like to test new drugs on. Although the technique of precisely control the differentiation is not mature yet, the usage of pluripotent stem cell does give scientists a bigger range of cell types to choose from. [59]
Use stem cells to test new drug is not only convenient, but also safer. Minger from the GE Healthcare said, “These are compounds which went all the way through animal testing, then went through phase I, II, III and then were licensed in many cases by the FDA.” Drug effects appeared on tested animals sometimes are very different when comes to human. But the new way of using stem cell testing is more accurate, and safe. When the compound in the new drug is with great toxicity, stem cells will be affected and will help scientists weed out the drugs with dangerous side effect. Get rid of the unqualified drugs before put it into mass production will help companies save large amount of money. [60]
Citation: 59,60


Present Application
Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by abnormal B or T lymphocytes, a kind of white cells, in the human immune system. When lymphoma occurs, the lymphocytes, which used to protect the body from infection and disease started populate lymph nodes.
There are two types of lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Compare to Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma is easier to be treated. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is usually treated by the combination of chemotherapy, monoclonal antibodies, immunotherapy, radiation, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. [61] For many lymphoma patients, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the best way to cure lymphoma once for all. If the patients responded well to the the chemotherapy, they can combine autologous stem cell transplantation (using stem cells from patients themselves) with chemotherapy. The 5 year survival rate of patients who used combination of both autologous stem cell transplantation and chemotherapy is 24% higher than patients who only used chemotherapy.
It is worth to notice that there are two kinds of stem cell transplantations in the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant. Autologous stem cell transplantation uses stem cells from the patients themselves, is a safer, better way to treat non-Hodgkin lymphoma. But after considered the patient’s condition, sometimes the doctor will suggest the patient having an Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant, in which case will use stem cells from a donor to do the transplantation. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation is still a controversial surgery. The problem comes from donor’s bone marrow. The donor’s bone marrow will form an immune system that only recognized the donor’s body, what ends up happening is, the patient’s new immune system might rejects patient’s body and an average of 15% of the patients die because of this rejection.
Although the treatment of stem cell transplantation still has a high percent of risk need to be taken by the patients, it is still the best way to treat non-Hodgkin lymphoma when the patient reach the standard. After all, chemotherapy and radiation can only cure the symptom, not the disease. [62]
Citation: 61,62

[57] Stage one Adult Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma

[56] The figure shows the non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma incidence rates by sex and age for the US male and female in 2007. The non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma incidence rates are per 100, 000 US population and are age-adjusted to the 2000 US Standard Population.

[58] Stage one Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma

[55]

[53] Leukemiasoluja
[52] The structure of human bone.
Molly Stevens: A new way to grow bone using the conbination of drug and human stem cell
One way to cure non-Hodgkin Lymphoma:
Cure for Leukemia:
[51]
[9]
[54] The Autologous Transplantation Processes.