Stem Cell

Stem Cells
[48]
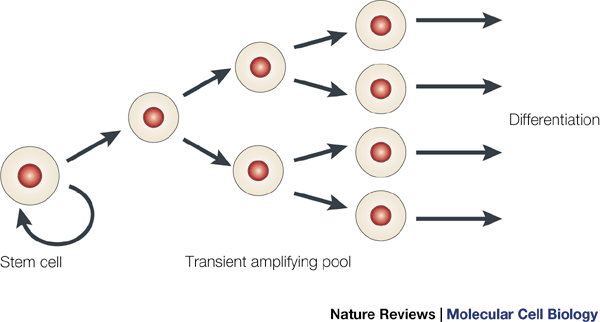

[2] Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into other different cell.Begin with the stem cell with the highest differentiate potential, the totipotent stem cell, it differentiate into multipotent stem cell and then into more specific cell.
[1 ] Stem cell's ability to differentiate
The differentiate potential stages
As stem cell developed, its differentiate potential becomes more restricted meaning that there are less cell type it can differentiated into. The 3 major differentiate potential order is
-
Totipotent
-
Pluripotent
-
Multipotent
The totipotent stem cell is usually refered to as the zygote, the fertilized egg, which can differentiate into pluripotent stem cell, as outer cell mass of blastocyst and extaembryonic tissues.
The pluripotent stem cell is usually a human embryonic stem cell or an Induced pluripotent stem cell. The pluripotent stem cell can give rise to all cell type in our body.
The multipotent stem cell comes after pluripotent stem in the differentiate potential order. They are usually adult tissue stem cell that can give rise to all cells in a specific tissue. For example, a multipotent blood stem cell can give rise to red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can self re-new and differentiate into other specific cells.
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells meaning that they do not have a specific function like a differentiated cell do. For example, a nerve cell is a differentiated cell and it is responsible for carring information.
While stem cells do not have any specific function, they are important for their ability to self multiply and become any cell through cell division. After the cell division, the new cell can become a new stem cell or differentiated cell. Stem cell’s ability to multiply and differentiate is vital for the body because with these characteristic, stem cell can replenish and repair many damaged cells in our body.
(1)
[50]
[49]
Click buttoms to learn about different types of stem cell
(Citation 1) (Citation 2) (Citation 3)