
Stem Cell
Policy in Different Countries
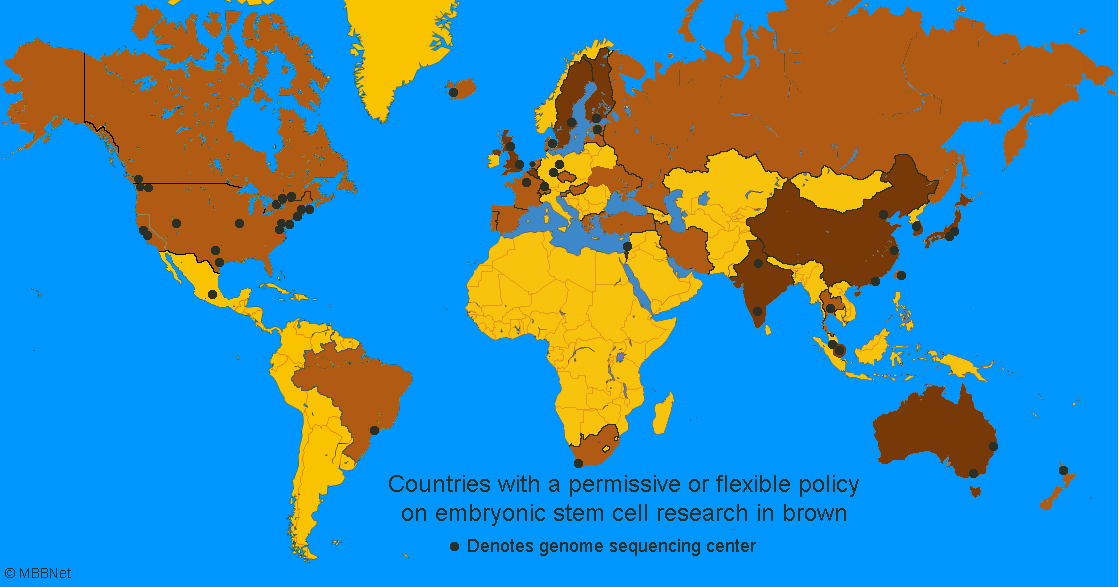
[36]The countries in brown have more permissive policy on stem cell research. The darker the brown the more permissive. The black dots show location with important stem cell research.
Australia, Belgium, China, India, Israel, Japan, Singapore, South Korea, Sweden, the United Kingdom are countries that have a highly permissive policy toward stem cell research. They allow embryonic stem cell research along with controversial techniques such as the somatic cell nuclear transfer.
Brazil, Canada, France, Iran, South Africa, Spain, The Netherlands, Taiwan have a flexible policy on stem cell research meaning that they have more restriction on stem cell research especially embryonic stem cell research.
Countries with a restrictive policy include Austria, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Norway, and Poland.
One example of the countries that has widely known for its permissive policy in stem cell research especially embryonic stem cell research is Japan. Stem cell research is strongly supported by Japanese government since the discovery of induce pluripotent stem cell by Dr. Shinya Yamanaka in 2007. With the support and fund from the government, many controversial research topics are permitted in Japan including the embryonic stem cell research and human somatic cell nuclear transfer and Japanese scientists are able to carry out large research project.

[37]
As an example of countries with flexable policy, France allows the use of embryos for scientific research but it has a strict regulation on the use of embryo for research. In order to have permission to use embryos in research, the scientist must prove that the research may bring important scientific breakthrough, the use of embryo is necessary and shows respect toward French ethical principle. After the research gained permission the permission the scientist still has to report to the French Biomedical Agency.
As an example of countries with a restrictive policy, Germany has completely banned embryonic stem cell research in Germany and Germany has made the derivation of embryonic stem cell line a criminal offense. The embryos are protected by German’s constitution with equal right of life as anyone else. The country also put strict regulation on importation of embryonic stem cell line in to Germany. Germany’s Stem Cell Act in 2002 requires that from 2002 and on any embryonic stem cell line that is imported into Germany must be derived prior to 2007. Furthermore, Germany also has a strict policy in other stem cell research. All important import stem cell line must be approved by Central Ethics Commission for Stem Cell Research.

[38]

[39]
(Citation 41) (Citation 42)